Researchers at the UCLA School of Dentistry have discovered a key molecule that allows cancer stem cells to bypass the body’s natural immune defenses, spurring the growth and spread of head and neck squamous cell cancers. But the study, conducted in mice, also demonstrated that inhibiting this molecule derails cancer progression and helps eliminate these stem cells.
These findings could help pave the way for more effective targeted treatments for this highly invasive type of cancer, which is characterized by frequent resistance to therapies, rapid metastasis, and a high mortality rate, the researchers said.
Also known as tumor-initiating cells, cancer stem cells are considered to be the original source of cancerous tissues, or the cells that give rise to all other cancer cells. Their ability to survive and proliferate in the early stages of cancer development, as well as during tumor growth and metastasis, suggests they have an intrinsic ability to evade detection by the body’s immune surveillance system. The researchers aimed to better understand how and why this happens.
When the immune system is functioning properly, the body’s natural infection-fighting T cells help to identify and ward off carcinogenic cells, foreign viruses, and other invaders. But some cancer cells elude this immune response by means of protein molecules on their surface known as checkpoints that bind to similar molecules on the T cells, nullifying the immune cells’ cancer-killing capabilities.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors can be administered to help rectify this. These drugs turn off the cancer cells’ checkpoint receptors, allowing T cells to perform their normal job. This approach has been effective in several types of cancer including melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer, decreasing the size of tumors and slowing their spread.
However, results have been mixed for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, indicating that something else may be occurring that mutes the immune system’s response, the researchers said.
To begin the study, the researchers tested a common checkpoint inhibitor that uses anti-PD1 antibodies on a well-defined mouse model of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. The drug did very little to slow the spread of the cancer, the researchers said.
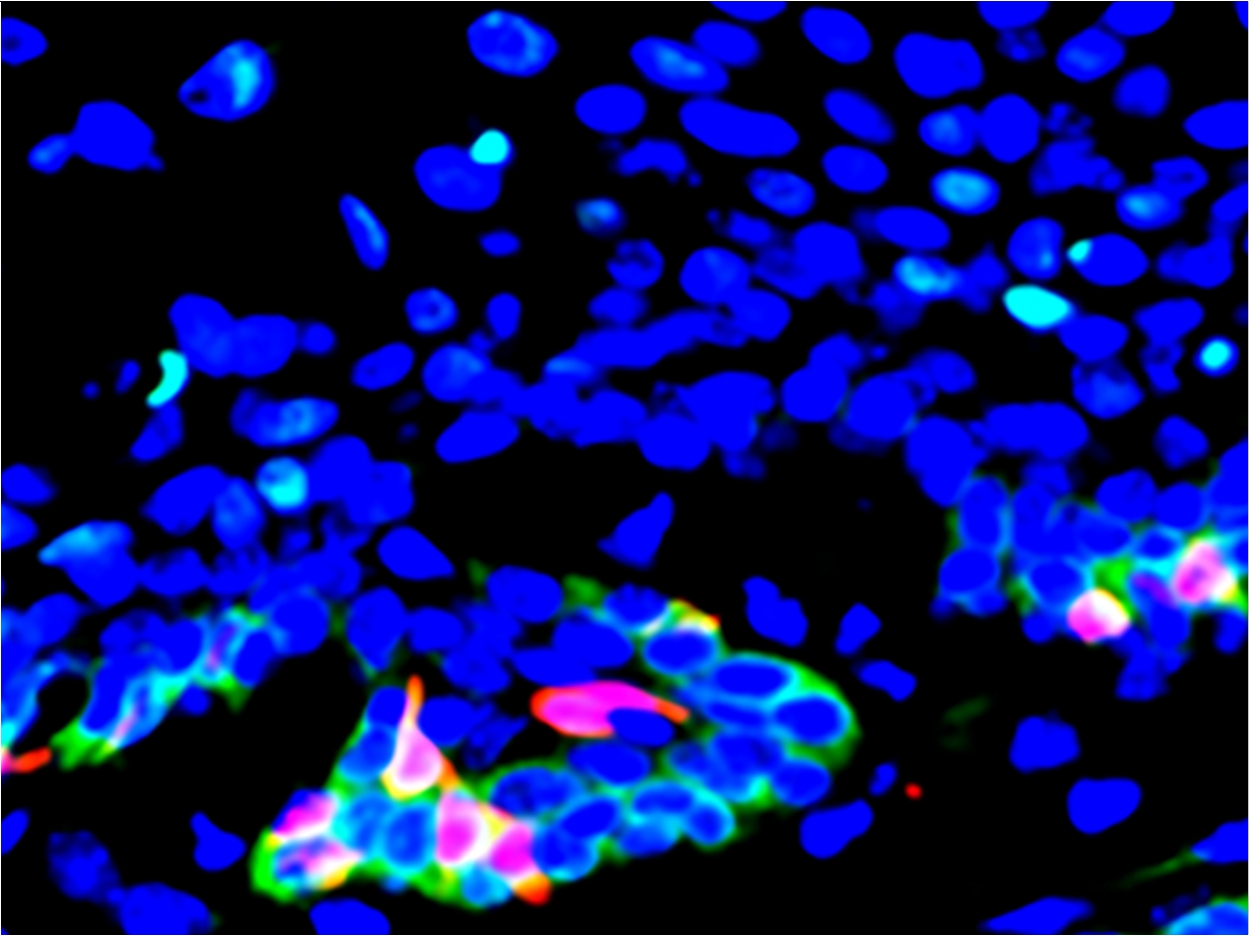
At the same time, they discovered that cancer stem cells in head and neck tumors had a notably elevated expression of the gene CD276, which encodes a protein molecule on the cell surface. They also found that CD276 expression was highest along the outer layers of tumors, suggesting that the CD276 molecule functions as a checkpoint that shields both the stem cells and cells in the interior of the tumor from the body’s T cell response to the cancer.
Similar to the use of checkpoint inhibitors, the researchers next administered anti-CD276 antibodies to a mouse model of the disease to see if this treatment could turn off the checkpoint and inhibit the growth and spread of the cancer. After a month, they witnessed a significant decrease in the number of cancerous lesions and cancer stem cells.
“Not only did we see a reduction in cancer stem cells and tumors in our model when we introduced the CD276 antibodies, but we also noticed that the total number of tumors that metastasized to the lymph nodes was significantly reduced,” said corresponding author Dr. Cun-Yu Wang, the Dr. No-Hee Park Professor of Dentistry and professor of oral biology and medicine.
“We were able to show that by blocking the gene CD276, we could effectively stop the growth of tumors derived from cancer stem cells,” said Wang, who also is a professor at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering and a member of the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center and the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA.
“These findings suggest that by focusing our attention on the CD276 gene and the immune response process, there is the potential for promising preventive therapeutic approaches against head and neck squamous cell carcinoma,” said coauthor Dr. Paul Krebsbach, dean of the UCLA School of Dentistry.
The study, “CD276 Expression Enables Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stem Cells to Evade Immune Surveillance,” was published by Cell Stem Cell.
Related Articles
Genetic Changes That Inhibit Head and Neck Cancer Immunotherapy Identified
Hydrogel Improves Oral Cancer Immunotherapy
Deactivation of Cancer Cell Gene Boosts Head and Neck Cancer Immunotherapy


