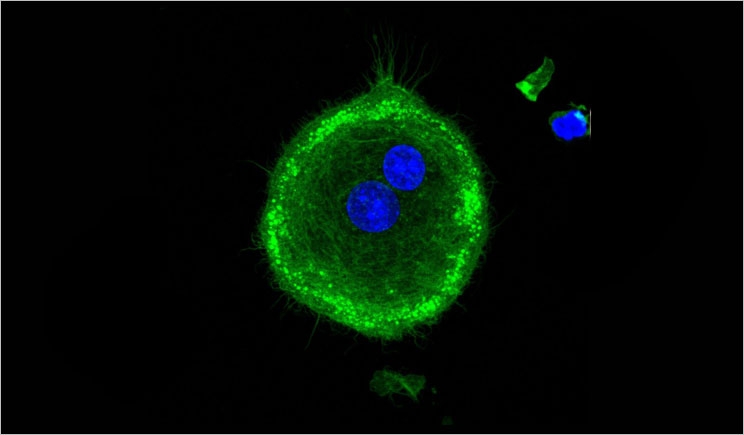
 There may be a definitive reason for people developing bone loss associated with gum disease or periodontitis. Adseverin, which is a protein found in the body, is a key factor in the bone loss that stems from common inflammatory diseases, according to the top biology journal FASEB. Researchers at the University of Toronto’s Faculty of Dentistry conducted this study, which focused on new preventive treatment models for these diseases. Periodontitis impacts millions of people each year. Roughly $125 million was spent in the United States during the last year to treat periodontitis. Periodontitis is considered an osteoimmune condition, similar to osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. These superosteoclasts cause damage as they form on the bone surface and eventually spit out enzymes that eat away the bone while loosening the teeth. When the osteoclasts are larger, they’re more effective at resorbing bone. To determine why this is the case, the researchers analyzed the role of cytokines, which are chemicals released by cells in the body. The research team concluded that the cytokines led to the production of Adseverin. The formation of supersosteoclasts relies on the presence of Adseverin, which also happens to be a rarity throughout the body. This study may provide the chance to look for new drugs for treating gum disease. It may also provide more information regarding bone loss that stems from osteoarthritis and osteoporosis.
There may be a definitive reason for people developing bone loss associated with gum disease or periodontitis. Adseverin, which is a protein found in the body, is a key factor in the bone loss that stems from common inflammatory diseases, according to the top biology journal FASEB. Researchers at the University of Toronto’s Faculty of Dentistry conducted this study, which focused on new preventive treatment models for these diseases. Periodontitis impacts millions of people each year. Roughly $125 million was spent in the United States during the last year to treat periodontitis. Periodontitis is considered an osteoimmune condition, similar to osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. These superosteoclasts cause damage as they form on the bone surface and eventually spit out enzymes that eat away the bone while loosening the teeth. When the osteoclasts are larger, they’re more effective at resorbing bone. To determine why this is the case, the researchers analyzed the role of cytokines, which are chemicals released by cells in the body. The research team concluded that the cytokines led to the production of Adseverin. The formation of supersosteoclasts relies on the presence of Adseverin, which also happens to be a rarity throughout the body. This study may provide the chance to look for new drugs for treating gum disease. It may also provide more information regarding bone loss that stems from osteoarthritis and osteoporosis.
Todays Dental News
Protein Could be Reason Behind Bone Loss in Osteoflammatory Disease
April 27, 20151 Mins read2.5k Views

This is an image of large, stained osteoclasts with adseverin.
0
Shares
0
Shares











